[Tensorflow] Keras Function API
in DeepLearning on Tech
tensorflow 기능적 API실습
기능적 API
keras모델을 하나 만들어보자 우선 입력노드를 생성하도록하자
inputs = keras.Input(shpae = (784,))
img_inputs = keras.Input(shape = (32,32,3))
inputs.shape
결과
TensorShape([None, 784])
이 inputs객체에서 레이어를 호풀하여 레이어 그래프에 새 노드를 만든다
dense = keras.Dense(64, activation = 'relu')
x = dense(inputs)
x = layers.Dense(64, activation="relu")(x)
outputs = layers.Dense(10)(x)
여기까지 완료하면 input과 output을 인수로가지는 모델을 만들 수 있다.
model = keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, name="mnist_model")
model.summary
결과:
Model: "mnist_model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 784)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 64) 50240
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 64) 4160
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 10) 650
=================================================================
Total params: 55,050
Trainable params: 55,050
Non-trainable params: 0
___________________________________________________________
이는 정리된 그림으로 볼수도 있는데
keras.utils.plot_model(model , "my first model" , show_shape = "True")
### 학습 , 평가 , 추론
학습과 평가 그리고 추론은 sequential모델을 구현하는 것과 같은 방식이다 MNIST 이미지데이터를 로드하고 벡터로 변형하고 데이터에 모델을 학습시킨 다음 테스트 데이터에서 모델을 평가한다.
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.reshape(60000, 784).astype("float32") / 255
x_test = x_test.reshape(10000, 784).astype("float32") / 255
model.compile(
loss=keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer=keras.optimizers.RMSprop(),
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64, epochs=2, validation_split=0.2)
test_scores = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=2)
print("Test loss:", test_scores[0])
print("Test accuracy:", test_scores[1])
케라스를 이용할때 학습순서는 데이터를 전처리한 후 model를 구축한다 그다음 model.compile를 통해 loss , optimizer 등을 설정해주고 model.fit을 통해 학습시킨다. 마지막으로 평가는 tset_scores = model.fit(x_tset, y_test, verbose=2)를 사용하여 얻어낼수 있다.
저장 및 직렬화
모델 저장및 직렬화는 기능적 API를 사용하여 빌드 된 모델에 대해 Sequenbtial모델과 동일한 방식으로 작동된다 model.save를 호출하여 전체모델을 단일 파일로 저장하는 것이다. 저장된 파일에는 1. 모델 아키텍처 2.모델 가중치 값 3.모델 학습 구성 4.optimizer상태 등이 포함된다.
model.save("path_to_my_model")
del model
# Recreate the exact same model purely from the file:
model = keras.models.load_model("path_to_my_model")
동일한 레이어 그래프를 사용하여 여러 모델정의
아래 예제에서는 동일한 레이어 스택을 사용하여 두 모델을 인스턴스화합니다. 하나는 이미지 입력을 16 차원 벡터로 변환하는 encoder 모델이고 다른 하나는 훈련을위한 엔드 autoencoder 엔드 autoencoder 모델이다.
encoder_input = keras.Input(shape=(28, 28, 1), name="img")
x = layers.Conv2D(16, 3, activation="relu")(encoder_input)
x = layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling2D(3)(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(16, 3, activation="relu")(x)
encoder_output = layers.GlobalMaxPooling2D()(x)
encoder = keras.Model(encoder_input, encoder_output, name="encoder")
encoder.summary()
x = layers.Reshape((4, 4, 1))(encoder_output)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(16, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(32, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.UpSampling2D(3)(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(16, 3, activation="relu")(x)
decoder_output = layers.Conv2DTranspose(1, 3, activation="relu")(x)
autoencoder = keras.Model(encoder_input, decoder_output, name="autoencoder")
autoencoder.summary()
결과
Model: "encoder"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
img (InputLayer) [(None, 28, 28, 1)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 26, 26, 16) 160
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 24, 24, 32) 4640
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) (None, 8, 8, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 6, 6, 32) 9248
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_3 (Conv2D) (None, 4, 4, 16) 4624
_________________________________________________________________
global_max_pooling2d (Global (None, 16) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 18,672
Trainable params: 18,672
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Model: "autoencoder"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
img (InputLayer) [(None, 28, 28, 1)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 26, 26, 16) 160
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 24, 24, 32) 4640
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d (MaxPooling2D) (None, 8, 8, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 6, 6, 32) 9248
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_3 (Conv2D) (None, 4, 4, 16) 4624
_________________________________________________________________
global_max_pooling2d (Global (None, 16) 0
_________________________________________________________________
reshape (Reshape) (None, 4, 4, 1) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_transpose (Conv2DTran (None, 6, 6, 16) 160
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_transpose_1 (Conv2DTr (None, 8, 8, 32) 4640
_________________________________________________________________
up_sampling2d (UpSampling2D) (None, 24, 24, 32) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_transpose_2 (Conv2DTr (None, 26, 26, 16) 4624
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_transpose_3 (Conv2DTr (None, 28, 28, 1) 145
=================================================================
Total params: 28,241
Trainable params: 28,241
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
모든 모델은 레이어처럼 호출 가능하다.
말 그대로 레이어의 출력에서 모델을 호출하여 모든 모델으 ㄹ레이어 인것처럼 처리 할 수 있다. 모델을 호출하면 모델의 아키텍쳐 뿐만아니라 가중치또한 재사용하게 된다 예시를 보자
encoder_input = keras.Input(shape=(28, 28, 1), name="original_img")
x = layers.Conv2D(16, 3, activation="relu")(encoder_input)
x = layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling2D(3)(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(16, 3, activation="relu")(x)
encoder_output = layers.GlobalMaxPooling2D()(x)
encoder = keras.Model(encoder_input, encoder_output, name="encoder")
encoder.summary()
decoder_input = keras.Input(shape=(16,), name="encoded_img")
x = layers.Reshape((4, 4, 1))(decoder_input)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(16, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(32, 3, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.UpSampling2D(3)(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(16, 3, activation="relu")(x)
decoder_output = layers.Conv2DTranspose(1, 3, activation="relu")(x)
decoder = keras.Model(decoder_input, decoder_output, name="decoder")
decoder.summary()
autoencoder_input = keras.Input(shape=(28, 28, 1), name="img")
encoded_img = encoder(autoencoder_input)
decoded_img = decoder(encoded_img)
autoencoder = keras.Model(autoencoder_input, decoded_img, name="autoencoder")
autoencoder.summary()
encoder모델과 decoder모델을 이용하여 autoencoder 모델을 구축하였다.
복잡한 그래프 토폴로지 조작
일반적인 Sequential API로 해결할 수 없는 문제또한 있을것이다 이러한 경우 나중에 알아보자 ㅎㅎ
장난감 ResNet 모델
위와같이 여러 입력 및 출력이 있는 모델 외에도 기능적 API를 사용하면 비선형 연결 토플로지를 쉽게 조작할 수 있다. 이는 잔여 연결을 통해 가능한데 이를 증명하기 위해 CIFAR10용 장난감 ResNet모델을 구축해 보겠다.
inputs = keras.Input(shape=(32, 32, 3), name="img")
x = layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation="relu")(inputs)
x = layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation="relu")(x)
block_1_output = layers.MaxPooling2D(3)(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(block_1_output)
x = layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(x)
block_2_output = layers.add([x, block_1_output])
x = layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(block_2_output)
x = layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation="relu", padding="same")(x)
block_3_output = layers.add([x, block_2_output])
x = layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation="relu")(block_3_output)
x = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
x = layers.Dense(256, activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.Dropout(0.5)(x)
outputs = layers.Dense(10)(x)
model = keras.Model(inputs, outputs, name="toy_resnet")
model.summary()
keras.utils.plot_model(model, "mini_resnet.png", show_shapes=True)
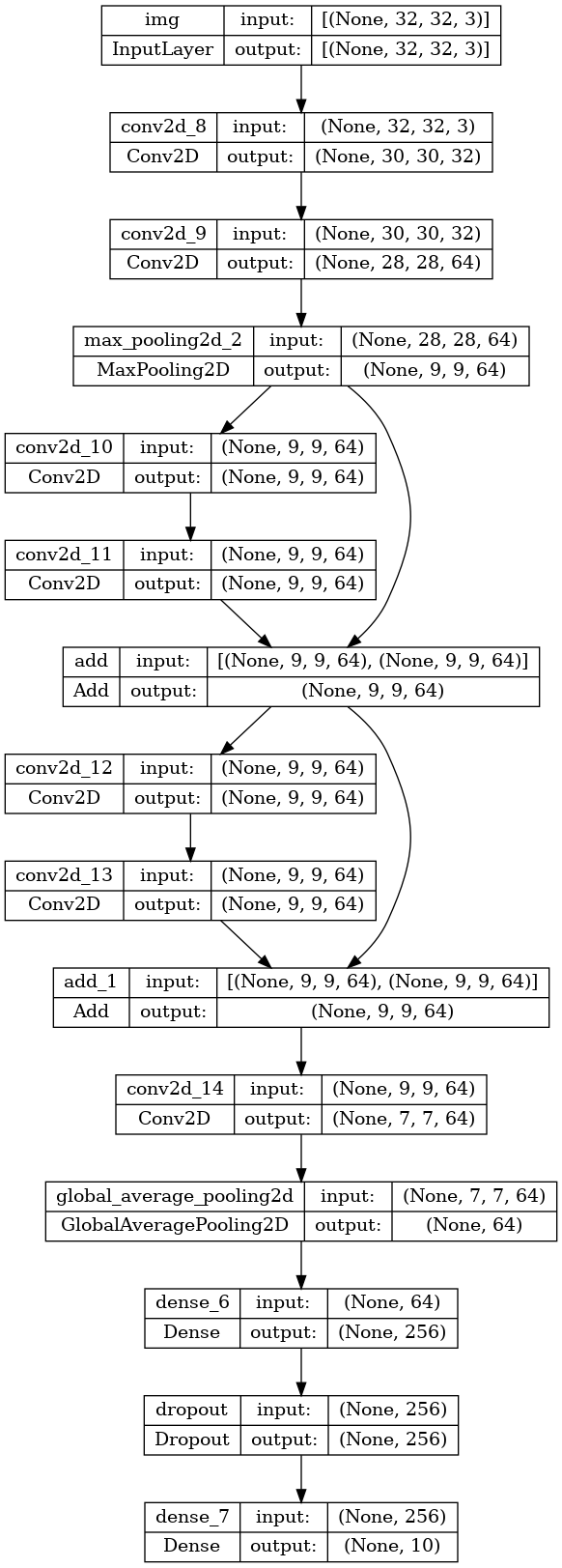
이제 모델을 학습 시키겠다
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.cifar10.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype("float32") / 255.0
x_test = x_test.astype("float32") / 255.0
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, 10)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, 10)
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.RMSprop(1e-3),
loss=keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=["acc"],
)
# We restrict the data to the first 1000 samples so as to limit execution time
# on Colab. Try to train on the entire dataset until convergence!
model.fit(x_train[:1000], y_train[:1000], batch_size=64, epochs=1, validation_split=0.2)
기능적 API의 또 다른 좋은 용도는 공유 레이어를 사용하는 모델이다 공유 레이어는 동일한 모델에서 여러번 재사용되는 레이어 인스턴스로, 레이어 그래프의
여러 경로에 해당하는 기능을 학습한다. 공유 레이어는 종종 유사한 공간에서 입력을 인코딩하는 데 사용된다. 이를 통해 서로 다른 입력간에 정보를 공유 할 수 있으며 더 적은 데이터로 이러한 모델을 훈련 할 수 있다. 주어진 단어가 입력 중 하나에 표시되면 공유 레이어를 통과하는 모든 립력 처리에 도움이 된다.
기능적 api에서 layer를 공유하려면 동일한 layer 인스턴스를 여러 번 호출하면 된다, 에를 들어 다음은 두가지 다른 텍스트 입력에서 공유되는 Embedding레이어 이다.
# Embedding for 1000 unique words mapped to 128-dimensional vectors
shared_embedding = layers.Embedding(1000, 128)
# Variable-length sequence of integers
text_input_a = keras.Input(shape=(None,), dtype="int32")
# Variable-length sequence of integers
text_input_b = keras.Input(shape=(None,), dtype="int32")
# Reuse the same layer to encode both inputs
encoded_input_a = shared_embedding(text_input_a)
encoded_input_b = shared_embedding(text_input_b)